Achieving data completeness is not just a best practice—it’s a must have in R&D, where experiments must be reproducible. By committing to comprehensive documentation and meticulous data collection, R&D teams can streamline processes, reduce redundant experiments, and foster innovation.
What Is Data Completeness?
Data completeness means capturing every possible detail that could influence the outcome of an experiment. From procedural steps to environmental conditions, nothing should be left undocumented. Incomplete data can lead to delays, increased costs, and missed opportunities. However, thorough documentation minimizes the experiments needed to reach a breakthrough.
Benefits of Achieving Data Completeness
- Enhanced Reproducibility: Complete data enables experiments to be replicated under identical conditions, building trust in results.
- Fewer Redundant Experiments: Comprehensive records reduce the need for repeated experiments, saving time and resources.
- Improved Collaboration: When every detail is captured, teams across departments or organizations can seamlessly pick up where others left off.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries require detailed records for audits and approvals. Data completeness simplifies compliance with these standards.
Download the Infographic and Save It For Your Experiments
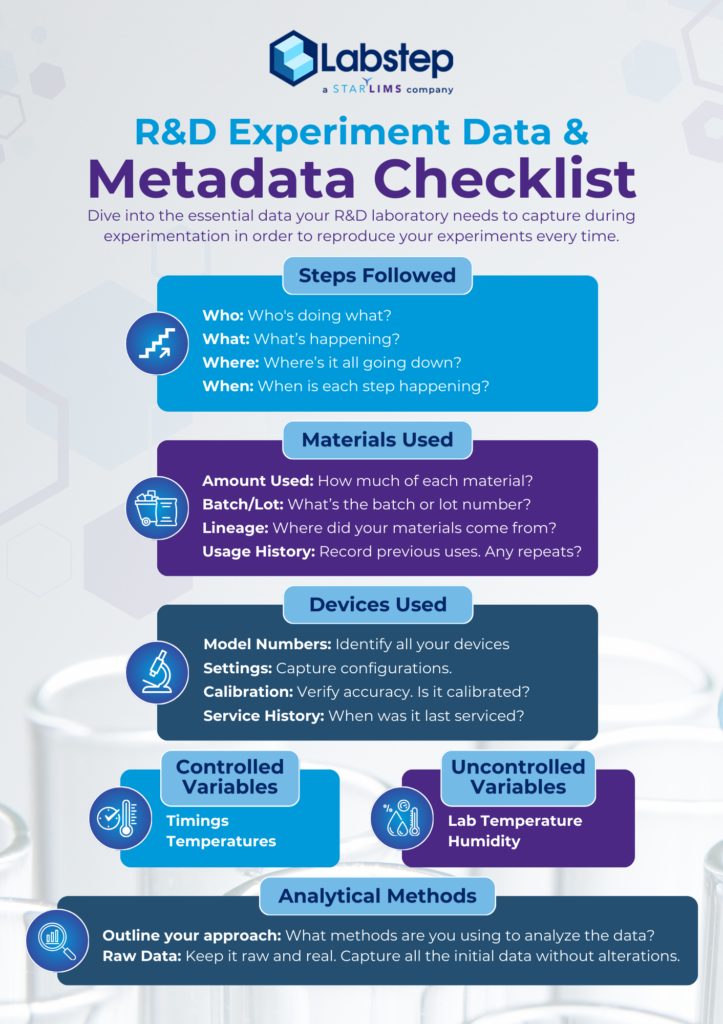
Essential Components of Data Collection in R&D
A comprehensive experiment record isn’t just about collecting information. It’s about making data is actionable, traceable, and meaningful. Below are key components of effective data collection:
- Who, What, Where, and When: Every experiment should clearly identify the personnel involved, the tasks performed, the location of the experiment, and the timeline for each step.
- Material Details: Document every material used, including batch or lot numbers, origin (lineage), previous usage, and the specific quantities employed. This traceability enables any variation in materials to be accounted for.
- Controlled and Uncontrolled Variables: Capture both the controlled variables like temperature and timing and the uncontrolled ones such as lab ambient conditions (e.g., humidity and general lab temperature).
- Equipment Information: Record the devices used, their model numbers, settings, calibration status, and service history. These details allow discrepancies in results to be traced back to potential equipment issues.
- Analytical Methods: Outline the data analysis techniques, so every transformation from raw data to final results is transparent and reproducible. Raw data should remain untouched, serving as the baseline for every interpretation.
In R&D, where time and resources are limited, data completeness is a foundation for thriving research. Every experiment is a story, and every detail—no matter how small—is a chapter that contributes to the whole narrative. By using technology and strategies that prioritize meticulous data collection and documentation, laboratories can improve reproducibility, reduce inefficiencies, and accelerate discovery.
You can use our infographic as a visual aid to reinforces these principles, or consider the Labstep ELN’s approach to data capture, which uses version controlled interactive protocols to assist scientists and researchers as they execute their experiments.

